Withania somnifera (root)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal Solanaceae
Standardized common name (English): ashwagandha
Ayurvedic name(s): ashvagandha
Botanical Voucher Specimen
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
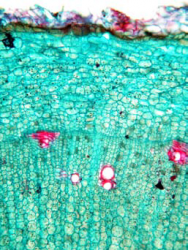
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
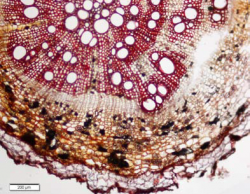
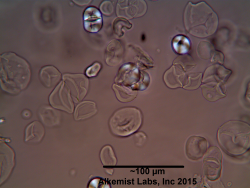
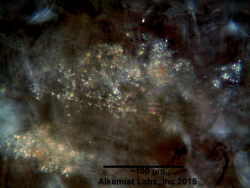
Microscopic Characteristics
|
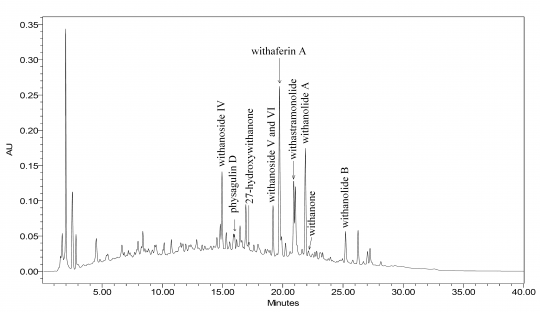
High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Identification
|
Ashwagandha (root) (Withania somnifera) Test Sample Preparation: Reflux for 20 minabout 5 g of coarse powdered plant material in 50 mL of methanol. Repeat the extraction 4-5times till the extract is nearly colorless. Combine the extracts and concentrate to about 100 mL.Before injection, filter through a 0.45-ummembrane filter. Column: 25-cm x 4.6-mm, 5 um, PhenomenexLuna C18(2) Mobile Phase: Dissolve 0.14 g of anhydrous potassium dihydrogen phosphate in 900 mL of water, add 0.5 mL phosphoric acid, mix, complete to volume with water, and mix (Solution A); and acetonitrile (Solution B) Elution: Gradient, see Table below Column Temperature: 25°C Flow rate:1.5 mL/min Detection: UV, 227 nm Injection volume: 20 uL Source: Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd [14]
Table: Gradient program
|
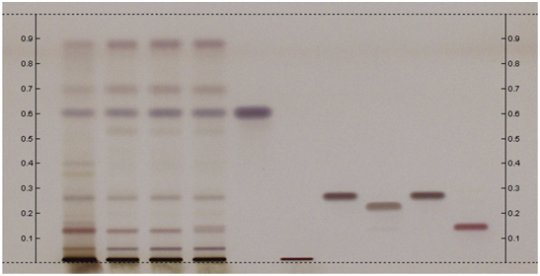
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Ashwagandha (root) (Withania somnifera) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Other Notes Reference Sample Preparations: Sonicate 0.5g of powdered sample in 5mL of methanol for 15 minutes, centrifuge or filter the solution, and use the supernatant / filtrate. Stationary Phase: HPTLC, Silica gel 60 F254 Mobile Phase: Toluene, ethyl acetate, acetic acid (55:45:3) Development: Saturated chamber, developing distance 70 mm from lower edge of the plate; relative humidity 33%, temperature 25°C. Derivatization reagent: Sulfuric Acid Reagent– 10% sulfuric acid in methanol (prepare fresh) Detection: Dip (time 0, speed 5) in Derivatization reagent, heat plate at 100°C for 5 min,and examine under visible light. Procedure: Reference Standard Solutions, Stationary Phase, Mobile Phase, Derivatization reagent, and Detection, as described above. Test Sample Preparation: Prepare test sample as described under Reference Sample Preparations andapply 10uL. Identification: Compare Test Sample Preparation chromatogram with chromatograms of Reference Sample Preparations. The Test SamplePreparation chromatogram is similar to that of the Reference Sample Preparations chromatograms. Additional weak zones may be present. The Test Sample Preparation chromatogram exhibits a grey-violet zoneand a brownish-violet zone at Rf corresponding to those of β-Sitosterol and withanolide A, respectively, in Reference Standard Solutionchromatogram, and two browninsh-violet zones in the lower third of the chromatogram at Rf lower than that corresponding to withanolide A in Reference Standard Solution chromatogram.
|
Supplementary Information
Detection of Aerial Parts in Extracts of Withania somnifera Roots
Deepak Mundkinajeddu, Laxman P. Sawant, Rojison Koshy, Praneetha Akunuri, Vineet Kumar Singh,1 Anand Mayachari, Maged H. M. Sharaf, Murali Balasubramanian, and Amit Agarwal
Introduction:
Withania somnifera root is considered to be the medicinally important part of the plant according to classical Ayurveda texts. The aerial parts, being less expensive, are sometimes mixed with roots to prepare extracts of W. somnifera. Both aerial parts and root show similar qualitative chromatographic fingerprints for the withanolides’ content, which tend to be the criterion to standardize these extracts.Unlike the withanolides content, flavonoid glycosides are unique constituents of the aerial parts and are absent in roots of the plant. These flavonoids include quercetin 3-O-robinobioside-7-O-glucoside,quercetin 3-O-rutinoside-7-O-glucoside, and kaempferol3-O-robinobioside-7-O-glucoside.
Procedure: Test Sample Preparation: Extract about 2 g of finely powdered plant material in 50 mL of methanol under reflux in a water bath for 20 min. Repeat the extraction 3 times. Combine the extracts and concentrate to about 100 mL. Before injection, filter through a 0.45-ummembrane filter.
Column: 25-cm x 4.6-mm, 5 um, PhenomenexLuna C18
Mobile Phase: Dissolve 0.14 g of anhydrous potassium dihydrogen phosphate in 900 mL of water, add 0.5 mL phosphoric acid, mix, complete to volume with water, and mix (Solution A); and acetonitrile (Solution B)
Elution: Gradient, see Table below
Column Temperature: 25°C
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Detection: UV, 350 nm
Injection volume: 20 uL
Detection of peaks corresponding to quercetin 3-O-robinobioside-7-O-glucoside (1), quercetin 3-O-rutinoside-7-O-glucoside (2), and kaempferol3-O-robinobioside-7-O-glucoside (3) indicates the presence of aerial parts.
Table: Gradient program
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0.0-12 | 90-80 | 10-20 |
| 12-18 | 80-55 | 20-45 |
| 18-25 | 55-20 | 45-80 |
| 25-28 | 20 | 80 |
| 28-35 | 20-55 | 80-45 |
| 35-40 | 55-90 | 45-10 |
| 40-45 | 90 | 10 |
Reference:
Mundkinajeddu D, Sawant LP, Koshy R, Akunuri P, Singh VK, Anand Mayachari, Sharaf MHM, Balasubramanian M, Agarwal A. Development and Validation of High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Flavonoid Glycosides in Withania somnifera Aerial Parts. ISRN Analytical Chemistry 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/351547 (accessed July 9, 2014)
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100184298
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19246862
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19246863
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19246864
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/