Glycyrrhiza glabra (root)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Fabaceae
Standardized common name (English): licorice
Ayurvedic name(s): yashtimadhu
Pinyin name(s): guang guo gan cao; gan cao (root & rhizome)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
|
|
|
|
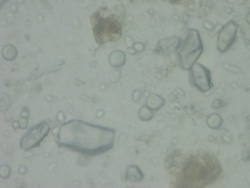
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
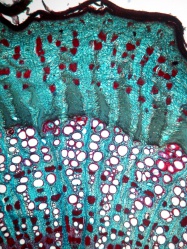
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
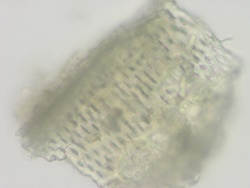
Microscopic Characteristics
|
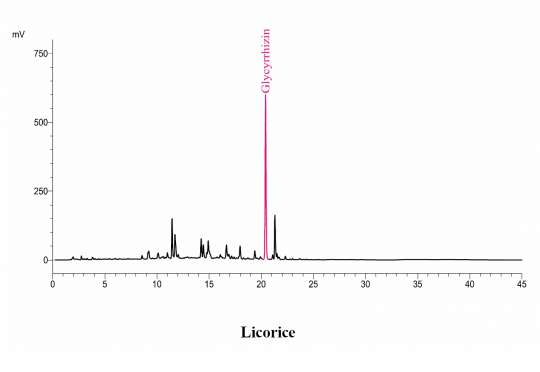
High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Identification
|
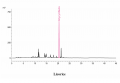
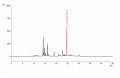
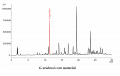
Licorice (root) (Glycyrrhiza glabra) Sample Preparations: Extract 1.0 g of coarsely powdered Glycyrrhiza root in 50 mL of water by boiling for about 5 minutes, and filter. Repeat for 4-5 times or until the extract is colorless. Combine the extracts, concentrate to about 100 mL, and cool to room temperature. Before injection, filter through a membrane filter of 0.45-um or finer pore size, discarding the first 5 mL of the filtrate. Column: C18, 25-cm x 4.6 mm, 5-um Mobile Phase: 0.14 g of anhydrous potassium dihydrogen phosphate in 900 mL of water, add 0.5 mL phosphoric acid, mix, complete to volume with water, and mix (Solution A); and acetonitrile (Solution B) Elution: Gradient program, see Table below Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min Detection: UV, 254 nm Injection volume: 20 uL Source: Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd [18] Table: Gradient program
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
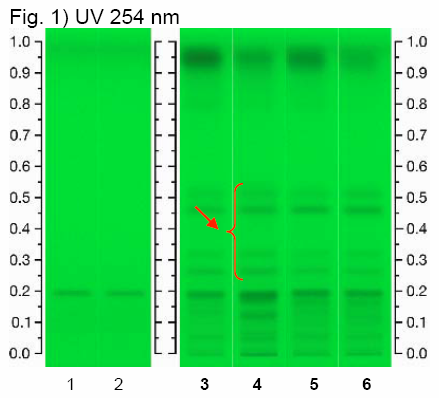
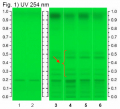
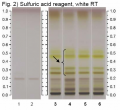
Licorice (root) (Glycyrrhiza glabra) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Other Notes Reference Sample Preparations: Mix 0.5 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of ethanol and water (7:3, v/v), sonicate for 10 minutes, centrifuge or filter the solution, and use the supernatant / filtrate. Stationary Phase: HPTLC, Silica gel 60 F254 Mobile Phase: Ethyl acetate, acetic acid, formic acid, water (15:1:1:2) Development: Saturate chamber for 20 minutes; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge of the plate; relative humidity 33%, temperature 25°. Derivatization reagent: Methanol sulfuric acid reagent- 180 mL of ice-cooled methanol are mixed with 20 mL of sulfuric acid. Detection: a. Examine under UV light at 254 nm b. Dip (time 0, speed 5) in Derivatization reagent, heat at 100°C for 10 min, leave to cool, and examine under visible light. Procedure: Reference Standard Solutions, Stationary Phase, Mobile Phase, Development, Derivatization reagent, and Detection, as described above. Test Sample Preparation: Prepare test sample as described under Reference Sample Preparations and apply 2 uL. Identification: Compare Test Sample Preparation chromatogram with chromatograms of Reference Sample Preparations. The Test Sample Preparation chromatogram is similar to that of the Reference Sample Preparations chromatograms. Additional weak zones may be present. Under UV light, the Test Sample Preparation chromatogram exhibits a quenching zone in the lower-third section of the chromatogram corresponding to the zone due to ammonium glycyrrhizate in the Reference Standard Solution chromatogram. Above it there are four quenching zones corresponding to those marked with red arrows in the Reference Sample Preparations chromatograms. After derivatization and under visible light, the Test Sample Preparation chromatogram exhibits a brown zone in the lower-third section of the chromatogram corresponding to the zone due to ammonium glycyrrhizate in the Reference Standard Solution chromatogram. Above it there are four yellow zones corresponding to those marked with black arrows in the Reference Sample Preparations chromatograms. Note: Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as a bases for setting specifications for quality control purposes. Source: HPTLC Association [19] |
Supplementary Information
Other Publications
HPLC with Online Near-IR analysis, Li, et al., 2015
Online near-infrared analysis coupled with MWPLS and SiPLS models for the multi-ingredient and multi-phase extraction of licorice (Gancao),
Abstract. This study aims to analyze the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) of licorice (Radix Glycyrrhizae; gancao), including glycyrrhizic acid, liquiritin, isoliquiritin and total flavonoids, in multi-ingredient and multi-phase extraction by online near-infrared technology with fiber optic probes and chemometric analysis. High-performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet spectrophotometry determined the APIs content in different extraction phases by online near-infrared analysis, which included sample set selection by the Kennard–Stone algorithm, optimization of spectral pretreatment methods (i.e., orthogonal signal correction and wavelet denoising spectral correction), and model calibration by the partial least-squares algorithm, moving-window partial least-squares algorithm and synergy interval partial least-squares (SiPLS) algorithm. The relative errors and F values were used to assess the models in different extraction phases. The root-mean-square error of correction, root-mean-square error of cross-validation and root-mean-square error of prediction of APIs in the SiPLS model was less than 0.07. The F values of glycyrrhizic acid, liquiritin, isoliquiritin and total flavonoids were 10,765, 32,431, 649 and 6080, respectively, which were larger than 6.90 (P < 0.01). The study demonstrated the feasibility of online NIR analysis in the multi-ingredient and multi-phase extraction of APIs from licorice. [20]
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100253567
- ↑ Trish Flaster, MSc, Botanical Liaisons, LLC http://www.BotanicalLiaisons.com
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ American Herbal Products Association. March 2013. Organoleptic Analysis of Herbal Ingredients. AHPA: Silver Spring, MD http://www.ahpa.org/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Flora von Deutschland, Österreich und der Schweiz- Otto Wilhelm Thomé (1885)
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/2447928
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/24932881
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19163752
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Hare, Caspari, Rusby. National Standard Dispensatory (1905)
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd http://www.naturalremedy.com/
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/
- ↑ Li, Y., Guo, M., Wu, Z., Li, J., Ma, Q., Qiao, Y. 2015. Online near-infrared analysis coupled with MWPLS and SiPLS models for the multi-ingredient and multi-phase extraction of licorice (Gancao) Chinese Medicine 10(38). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13020-015-0069-2
- Botanical
- Fabaceae
- Media
- Voucher
- MOBOT, Tropicos.org
- Trish Flaster, MSc, Botanical Liaisons, LLC
- Organolepsy
- Natural Remedies Pvt Ltd
- American Herbal Products Association. March 2013. Organoleptic Analysis of Herbal Ingredients. AHPA: Silver Spring, MD
- Macroscopy
- PlantaPhile
- Microscopy
- Hare, Caspari, Rusby. National Standard Dispensatory (1905)
- HPTLC
- HPTLC Association