Cinnamomum aromaticum (bark)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Cinnamomum aromaticum Nees Lauraceae
Syn. Cinnamomum cassia auct.
Standardized common name (English): cassia
Pinyin name(s): rou gui; rou gui (bark); gui zhi (twig)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
|
Microscopic Characteristics
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
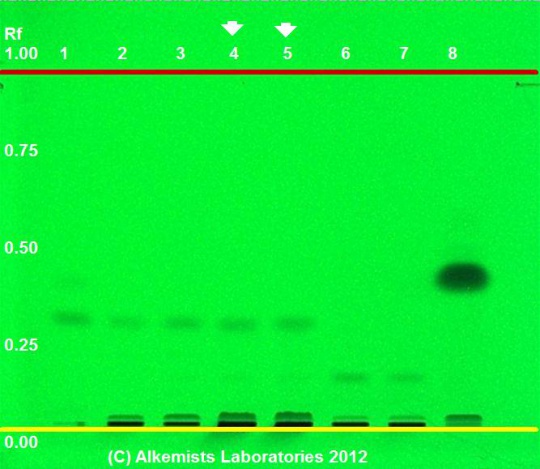
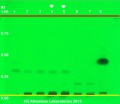
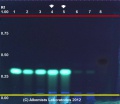
Cassia (bark) (Cinnamomum aromaticum Nees) Lane Assignments Lane 2(3μl) Cinnamomum aromaticum / Cinnamomum cassia (bark); Lane 3(3μl) Cinnamomum aromaticum / Cinnamomum cassia (bark); Lane 6(3μl) Cinnamomum verum (bark); Lane 7(3μl) Cinnamomum verum (bark) authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below, held at Alkemists Pharmaceuticals, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase toluene: ethyl acetate [9.5/0.5] Sample Preparation Method 0.3g+3mL CH3OH sonicate/heat @~50° C ~ 1/2 hr. Detection Method Image 1 UV 254 nm; Image 2 10% Ethanolic KOH Reagent 365 nm Reference see Method Developed by Alkemist Laboratories Source: Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories [5] |
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com