Capsicum annuum (fruit)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Capsicum annuum L. var. annuum Solanaceae
Syn. Capsicum frutescens L.
Standardized common name (English): cayenne
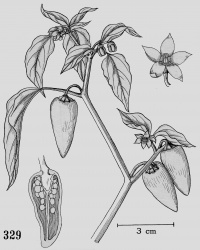
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
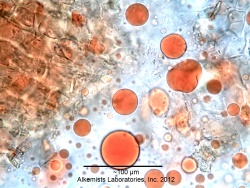
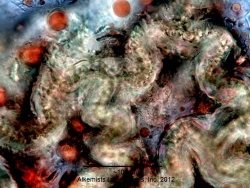
Microscopic Characteristics
|
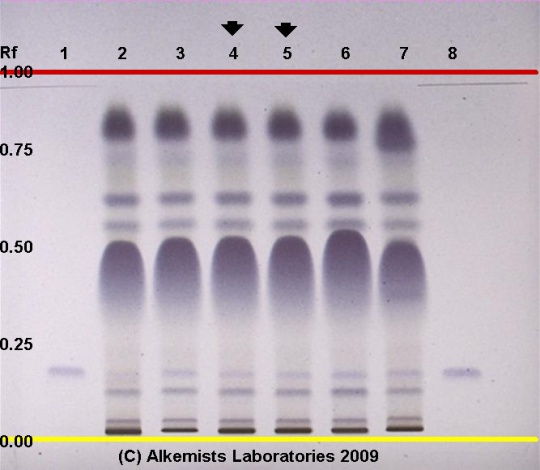
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Cayenne (fruit) (Capsicum annuum var. annuum L.) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase toluene: ethyl acetate [7/3] Sample Preparation Method 0.5g+5ml dichloromethane, sncte/cntrfge/dcnt, evap dry (N2), qs 1.0 ml Toluene Detection Method Vanillin/H2SO4 Reagent -> 110° C 5 min -> Visible light Reference see British Herbal Pharmacopoeia, 1996
|
|
Cayenne pepper (fruit) (Capsicum annum / Capsicum frutescens) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 2 mg of capsaicin in 5 mL of methanol. Dissolve 2 mg of dihydrocapsaicin in 5 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, RP-18, F254 Mobile Phase Water, methanol 20:80 (v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Derivatization reagent: Dichloroquinone chlorimide reagent Preparation: 50 mg dichloroquinone chlorimide in 200 mL of ethyl acetate Use: Dip (time 0, speed 5), dry with cold air for 5 min, then expose to ammonia vapor Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Capsaicin: blue zone at Rf ~ 0.47; Dihydrocapsaicin: blue zone at Rf ~ 0.40 Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. The chromatogram of the test solution shows two blue zones at Rf ~ 0.40 and Rf ~ 0.47.
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100018388
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000592613
- ↑ Culbreth, D. (1917) A Manual of Materia Media and Pharmacology, 6th ed.
- ↑ Culbreth, D. (1917) A Manual of Materia Media and Pharmacology, 6th ed.
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/83419
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Culbreth, D. (1917) A Manual of Materia Media and Pharmacology, 6th ed.
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/