|
AHPA recognizes other valuable resources exist regarding the identity of Acacia senegal.
To submit a suggestion or contribution, please contact Merle Zimmermann.
|
Nomenclature
Acacia senegal (L.) Willd. Fabaceae
Standardized common name (English): gum arabic tree
Botanical Voucher Specimen
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Texture A meal. Should not be lumpy or in sticky masses.
Color White to nearly snow white.
Scent Nearly odorless.
Flavor Mucilaginous taste, sticky.
Source: Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed. [4]
|
|
|
|
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
| The most important of the gum-yielding Acacias is the official A. Senegal Willd.
This is a small tree rarely exceeding a height of 6 m., with a grayish bark, the inner layers of which are strongly fibrous, bipinnate leaves, dense spikes of small yellow flowers longer than the leaves, and broad pods containing 5 or 6 seeds.
The gum of the acacias exudes spontaneously from the bark, and hardens on exposure; but incisions are sometimes made in order to facilitate the exudation. The gum is said also to be found immediately under the bark, where it is sometimes collected in regular cavities. It is formed within the plant by metamorphosis of the cells of the inner bark. The tissues involved are chiefly those of the sieve and the cambiform cells.
Source: United States Dispensatory (1918) [5]
|
|
|
|
|
Microscopic Characteristics
| Acacia senecal dried brittle glassy gummy exudation. AKA Gum Arabic.Shows no structure under the microscope. Reduce some of the gum to fine powder and dissolve about five grams in 10 parts water; centrifuge for a short time and examine the sediment for impurities which are usually present, consisting of trace of starch, some dirt and bits of vegetable tissue.
Source: Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed. [6]
|
|
|
|
|
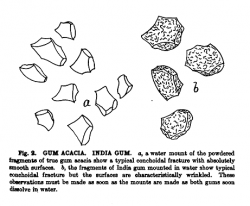
Source: Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.[7]
|
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100191277
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000791160
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000791161
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.
- ↑ Schneider, A. (1921) The Microanalysis of Powdered Vegetable Drugs, 2nd ed.





