Equisetum palustre (leaf)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
Macroscopic Characteristics
Microscopic Characteristics
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
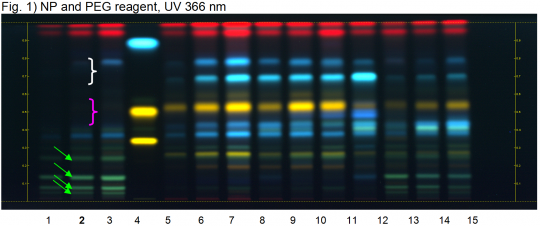
Marsh horsetail herb (leaf) (Equisetum palustre) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Individually dissolve 1 mg of caffeic acid, 1 mg of rutin, and 1 mg of hyperoside each in 1 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Ethyl acetate, water, acetic acid, formic acid 134:36:15:15 (v/v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 1 g of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Derivatization reagent: NP reagent, Preparation: 1 g of natural products reagent in 200 mL of ethyl acetate; 2.) PEG reagent, Preparation: 10 g of polyethylene glycol 400 in 200 mL of methylene chloride, Use: Heat plate for 3 min at 100°C, dip (time 0, speed 5) in NP reagent, dry and dip (time 0, speed 5) in PEG reagent. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Rutin: orange fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.34; Hyperoside: orange fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.50; Caffeic acid: light blue fluorescent zone at Rf ~ 0.88. Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. The chromatogram of the test solutions shows four green zones between the application position and the zone due to reference substance rutin (green arrows). Right above the zone due to rutin there is a faint blue zone. Just below the solvent front there are two red zones due to chlorophylls. Test for adulteration: There is no yellow zone at or right above the position of hyperoside (pink arrow); between hyperoside and caffeic acid there are not two intense blue zones (white arrow, Common horsetail herb).
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K001057681
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/