Carthamus tinctorius (flower)
Contents |
Nomenclature
Carthamus tinctorius L. Asteraceae
Standardized common name (English): safflower
Ayurvedic name(s): kusumbha
Pinyin name(s): hong hua (flower)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
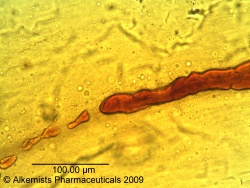
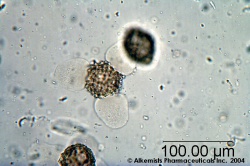
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
|
|
|
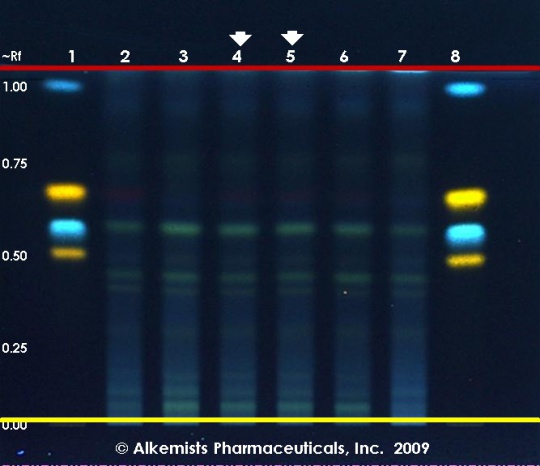
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Safflower (flower) (Carthamus tinctorius) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase ethyl acetate: AcCOOH: HCOOH: H2O [10/1.1/1.1/2.4] Sample Preparation Method 0.3 g + 3 ml CH3OH sonicated + heated @ 50° C ~ 1 hr Detection Method Natural Product Reagent + PEG -> UV 365 nm Reference see Adapted from Plant Drug Analysis, Wagner, H., 1996
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com