|
AHPA recognizes other valuable resources exist regarding the identity of Panax ginseng.
To submit a suggestion or contribution, please contact Merle Zimmermann.
|
Nomenclature
Panax ginseng C.A. Mey. Araliaceae
Syn. Panax schinseng T. Nees
Standardized common name (English): Asian ginseng
Pinyin name(s): ren shen (root)
Botanical Voucher Specimen
Organoleptic Characteristics
[Panax ginseng (root)] has a feeble odor, and a sweet, slightly aromatic taste, somewhat analogous to that of licorice root.
Source: United States Dispensatory (1918) [1]
|
|
|
|
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
| The root is fleshy, somewhat spindle-shaped, from 5 to 12 cm. long, and 1 to 2.5 cm. thick, and terminated by one or more stem scars. Frequently there are two portions, sometimes three or more, connected at their upper extremity, and bearing a supposed, though very remote, resemblance to the human figure, from which circumstance it is said that the Chinese name ginseng originated. When dried, the root is yellowish-white and wrinkled externally, and within consists usually of a hard central portion, surrounded by a soft whitish bark.
Source: United States Dispensatory (1918) [2]
|
|
|
|
 |
|

Source: PlantaPhile[3]
|
|
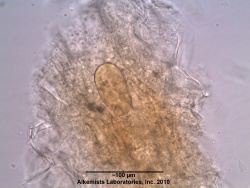
Microscopic Characteristics
| Cellular structures identified in Panax ginseng root are the rosettes of calcium oxalate and yellow secretion from a resin canal when observed at 400x with Acidified Chloral Hydrate Glycerol Solution.
Source: Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories [4]
|
|
|
|
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
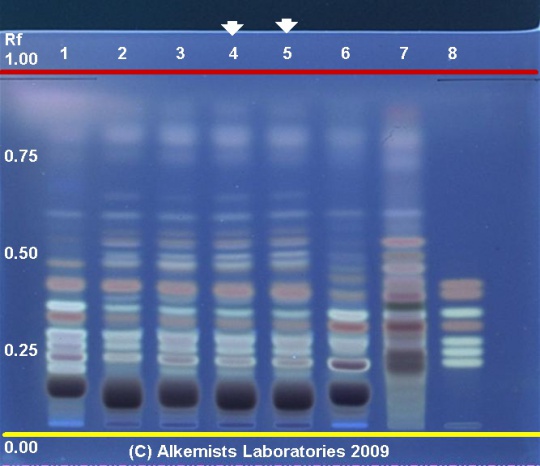
Panax ginseng HPTLC ID - 10% Methanolic Sulfuric Acid UV 365 nm
Asian Ginseng (root) (Panax ginseng)
Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-1 (root)
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-2 (root)
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-3 (root)
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-4 (root)
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-4 (root)
- 2 μL Panax quinquefolius-5 (root)
- 2 μL Panax ginseng-6 (root)
- 2 μL Ginsenoside-Rb1, Ginsenoside-Rc, Ginsenoside-Rd, Ginsenoside-Re, Ginsenoside Rf, Ginsenoside-Rg1 ~0.1% in MeOH
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA.
Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates
Mobile Phase chloroform: ethyl acetate: CH3OH: water [3/8/4.4/1.8]
Sample Preparation Method 0.3 g + 3 ml 70% grain EtOH sonicate 10 minutes no heat
Detection Method 10% Methanolic H2SO4 -> 115° C 15 min -> UV 365 nm
Reference see American Herbal Pharmacopoeia & Therapeutic Compendium
Source: Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories [7]
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com