Camellia sinensis (leaf)
(add HPLC reference) |
(add method headers) |
||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
|} | |} | ||
=Liquid Chromatographic Identification= | =Liquid Chromatographic Identification= | ||
| + | ==UPLC Method== | ||
{| border=1 | {| border=1 | ||
|{{Botanical | source=Indena S.p.A. | |{{Botanical | source=Indena S.p.A. | ||
| Line 171: | Line 172: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | ==HPLC Method== | ||
[[Category:HPLC]] | [[Category:HPLC]] | ||
{| border=1 | {| border=1 | ||
Latest revision as of 14:46, 30 October 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze Theaceae
Syn. Thea sinensis L.
Standardized common name (English): tea
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
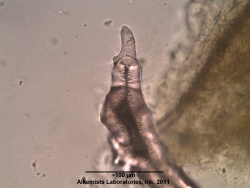
Microscopic Characteristics
|
Liquid Chromatographic Identification
UPLC Method
|
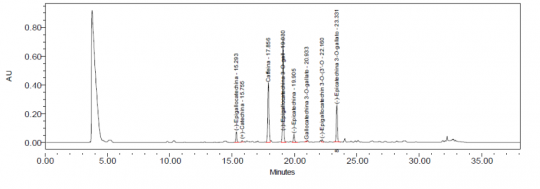
Camellia sinensis (leaf) UPLC Extraction Solvent: Acetone & water (80:20) Diluent: 0.5% formic acid in water Test Sample Preparation: Transfer 1 g of ground plant material into a screw cap bottle, add 50 ml of Extraction Solvent, tightly cap, and shake for 4 h in a mechanical shaker at room temperature. Filter about 10 ml of extract using a 0.20 um PTFE membrane filter. Dilute 2.0 ml of filtered solution to 10 mL with Diluent. Column: 100 mm x 2.1 mm, 1.7 um, Waters Acquity BEH C18 Mobile Phase: 0.5% formic acid in acetonitrile (Solution A) and 0.5% formic acid in water (Solution B) Elution: Gradient, see Table below Column Temperature: 30°C Flow rate: See Table below Detection: UV, 274 nm Injection volume: 1.0 uL, maintained at 10°C Needle wash: Acetonitrile Source: Indena S.p.A. [19] Table: Gradient program
|
HPLC Method
|
Camellia sinensis (leaf) HPLC Extraction Solvent: Acetone, water (80:20) Diluent: 0.05% formic acid in water Test Sample Preparation: Transfer 1 g of ground plant material into a screw cap bottle, add 50 ml of Extraction Solvent, tightly cap, and shake for 4 h in a mechanical shaker at room temperature. Filter about 10 ml of extract using a 0.20 um PTFE membrane filter. Dilute 2.0 ml of filtered solution to 10 mL with Diluent. Column: 15-cm x 4.6-mm, 3 um, YMC-Pack ODS-A Mobile Phase: 0.05% formic acid in water (Solution A), 0.05% formic acid in methanol (Solution B), and acetonitrile (Solution C) Elution: Gradient, see Tables below Column Temperature: 40°C Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min Detection: UV, 274 nm Injection volume: 10 uL Source: Indena S.p.A. [20] Table for HPLC systems with dwell volume ˂ 2.0 mL
Table for HPLC systems with dwell volume > 4.0 mL
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
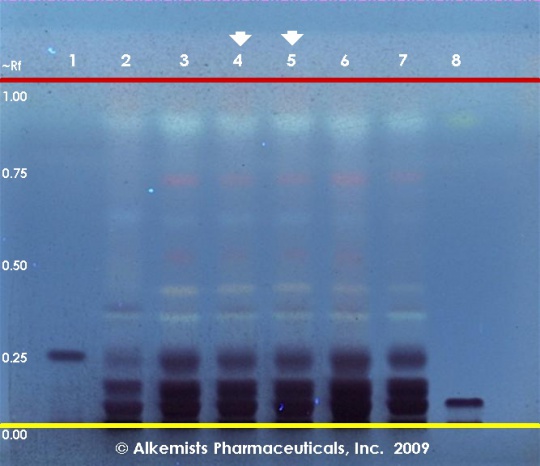
Green Tea (leaf) (Camellia sinensis) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase CHCl3: ethyl formate: HCOOH [5/4/1] Sample Preparation Method 0.3 g + 3ml 70% grain EtOH sonicated + heated @ 50° C ~ 1 hr Detection Method Vanillin/H2SO4 Reagent -> 110° C 5 min -> UV 365 nm Reference see Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals, Wichtl, M., 1994
|
|
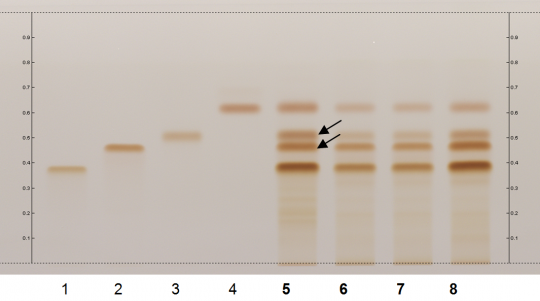
Green Tea (leaf) (Camellia sinensis) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference:Individually dissolve 1 mg of (-)-epigallocatechin and 1 mg of (-)-epicatechin gallate each in 20 mL of methanol; Optional: Individually dissolve 1 mg of (-)-epigallo-catechin-3-O-gallate and 1 mg of (-)-epicatechin each in 20 mL of methanol; Store all solutions at -20°C. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Toluene, acetone, formic acid 9:9:2 (v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 100 mg of powdered sample with 10 mL of methanol, water 4:1 and sonicate for 10 minutes, then centrifuge or filter the solutions and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Derivatization reagent: Fast Blue salt B reagent; Preparation: dissolve 140 mg of Fast Blue salt B in 10 mL of water and add 140 mL of methanol and 50 mL of dichloromethane. Store reagent in the dark at 4°C; Use: preheat the plate to 100°C for 2 min, then dip (time 0, speed 5), dry for 5 min in the fume hood. Detection Method Unsaturated chamber; developing distance 60 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: (-)-Epigallocatechin: brown zone at Rf ~ 0.46; (-)-Epicatechin gallate: brown zone at Rf ~ 0.52 Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. The chromatogram of the test solution shows four brownish-orange zones corresponding to reference substance epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (Rf ~ 0.37), (-)-epigallocatechin (Rf ~ 0.46), (-)-epicatechin gallate (Rf ~ 0.52), and (-)-epicatechin (Rf ~ 0.62). The lowest zone is the most intense and the upper zone is the faintest. The two zones in between are clearly separated (black arrows).
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org. http://www.tropicos.org/Image/30076
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org. http://www.tropicos.org/Image/30070
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org. http://www.tropicos.org/Image/30074
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000894813
- ↑ American Herbal Products Association. March 2013. Organoleptic Analysis of Herbal Ingredients. AHPA: Silver Spring, MD
- ↑ Clayton et al. Compendium of food microscopy (1909).
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/2445507 http://eol.org/data_objects/2445507
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19242832 http://eol.org/data_objects/19242832
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/25801092 http://eol.org/data_objects/25801092
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data_objects/19242831 http://eol.org/data_objects/19242831
- ↑ Köhler, Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen und kurz erläuterndem Texte (1887)
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Clayton et al. Compendium of food microscopy (1909).
- ↑ Greenish, H. et. al. (1908) An Anatomical Atlas of Vegetable Powders
- ↑ Amy Brush, Traditional Medicinals http://www.traditionalmedicinals.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Greenish, H. et. al. (1908) An Anatomical Atlas of Vegetable Powders
- ↑ Indena S.p.A. http://www.indena.com/
- ↑ Indena S.p.A. http://www.indena.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/
- Botanical
- Theaceae
- Media
- Voucher
- MOBOT, Tropicos.org.
- Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- Macroscopy
- American Herbal Products Association. March 2013. ''Organoleptic Analysis of Herbal Ingredients.'' AHPA: Silver Spring, MD
- Clayton et al. ''Compendium of food microscopy'' (1909).
- Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data objects/2445507
- Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data objects/19242832
- Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data objects/25801092
- Encyclopedia of Life http://eol.org/data objects/19242831
- Köhler, Medizinal-Pflanzen in naturgetreuen Abbildungen und kurz erläuterndem Texte (1887)
- Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- Microscopy
- Greenish, H. et. al. (1908) An Anatomical Atlas of Vegetable Powders
- Amy Brush, Traditional Medicinals
- Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories
- Indena S.p.A.
- HPLC
- HPTLC
- HPTLC Association