Hypericum perforatum (flowering tops)
(Botanical Voucher Kew added) |
(add USD 1918 organoleptic information) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
=Organoleptic Characteristics= | =Organoleptic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {{Organolepsy | source=United States Dispensatory (1918) | ||
| + | | description=[''Hypericum perforatum'' ...] a peculiar balsamic odor, which is rendered more sensible by rubbing or bruising the plant. Its taste is bitter, resinous, and somewhat astringent.}} | ||
=Macroscopic Characteristics= | =Macroscopic Characteristics= | ||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 17 March 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Hypericum perforatum L. Clusiaceae
Standardized common name (English): St. John's wort
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
|
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
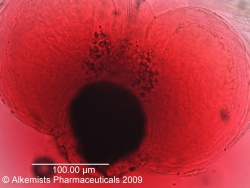
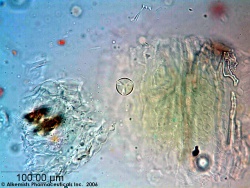
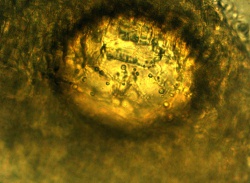
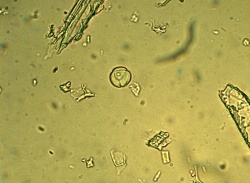
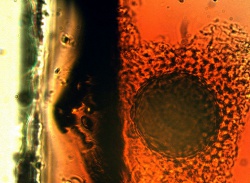
Microscopic Characteristics
|
High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Identification
|
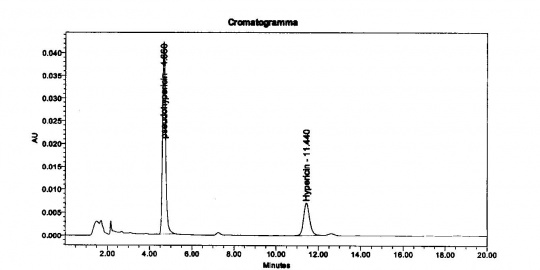
'Method for Hypericins Column: 15-cm x 4.6 mm, 5-um, Waters Atlantis C18 Mobile Phase: A mix of 39 volumes of ethyl acetate, 41 volumes of a 15.6 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate adjusted to pH 2 with phosphoric acid and 160 volumes of methanol. Elution: Isocratic Column Temperature: 40°C Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min Detection: Vis, 590 nm Injection volume: 20 uL Source: Indena S.p.A. [20] |
|
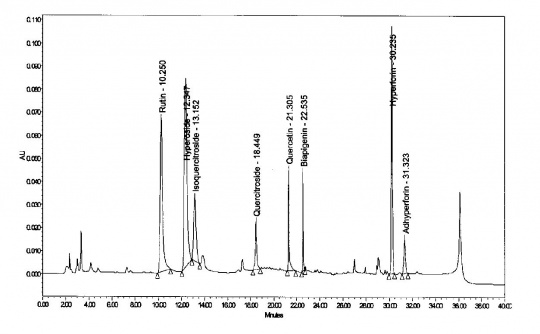
'Method for Hyperforins and Flavonoids Column: 15-cm x 4.6 mm, 3-um, YMC-Pack ODS-A Mobile Phase: Water, containing 0.3 % (v/v) phosphoric acid 85% (Solution A) and acetonitrile containing 0.3 % (v/v) phosphoric acid 85% (Solution B) Elution: Gradient, see table below Column Temperature: 25°C Detection: UV, 360 nm, then at 275 nm after the elution of biapigenin (about 22 min) Injection volume: 10 uL Source: Indena S.p.A. [21] Table: Gradient program
|
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
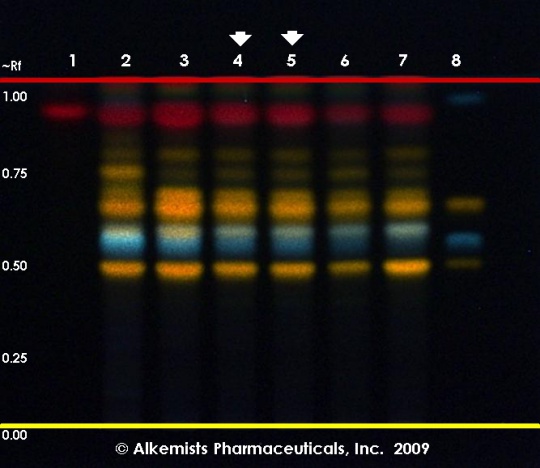
St. John's wort (herb) (Hypericum perforatum) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Other Notes Reference Sample Preparations: Sonicate 0.5 g of powdered sample in 5 mL of methanol at 60°C, centrifuge or filter the solution, and use the supernatant / filtrate. Stationary Phase: HPTLC, Silica gel 60 F254 Mobile Phase: Ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, water, formic acid, acetic acid (100:25:11:10:10) Development: Saturate chamber for 20 minutes; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge of the plate; relative humidity 33%, temperature 25°. Derivatization reagent A: Natural Products Reagent (NP)– 5 mg/mL 2-aminoethyl diphenylborinate in ethyl acetate in a glass bottle. Derivatization reagent B: PEG Reagent– 50 mg/mL polyethylene glycol 400 (macrogol) in dichloromethane in a glass bottle. Detection: Heat plate at 100°C for 3 min, dip (time 0, speed 5) in Derivatization reagent A, dry, dip (time 0, speed 5) in Derivatization reagent B, and examine under UV light at 366 nm. System suitability: Rutin: orange fluorescent zone in the lower one-third of the plate at about Rf 0.1. Hyperoside: orange fluorescent zone in the lower one-third of the plate at about Rf 0.25. Procedure: Reference Standard Solutions, Stationary Phase, Mobile Phase, Development, Derivatization reagent A, Derivatization reagent B, and Detection, as described above. Test Sample Preparation: Prepare test sample as described under Reference Sample Preparations and apply 4 uL. Identification: Compare Test Sample Preparation chromatogram with chromatograms of Reference Sample Preparations. The Test Sample Preparation chromatogram is similar to that of the Reference Sample Preparations chromatograms. Additional weak zones may be present. The Test Sample Preparation chromatogram exhibits fluorescent zones corresponding to the zones due to rutin, hyperoside, hypericin, and pseudohypericin in the Reference Standard Solution chromatograms. Between the zones due to hyperoside and hypericin there are several orange fluorescent zones. Related Species: A very faint zone at the Rf corresponding to rutin indicating Hypericum montanum (mountain St. John’s Wort), Hypericum hirsutum (hairy St. John’s Wort), or Hypericum undulatum (wavy St. John’s Wort). A blue fluorescent zone detected below and well resolved from the hyperoside zone indicating Hypericum montanum. Two yellow zones detected around one-third of the chromatogram indicating Hypericum hirsutum. An orange zone detected at Rf 0.47 indicating Hypericum undulatum. Note: Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as a bases for setting specifications for quality control purposes.
|
|
St. John's Wort (herb) (Hypericum perforatum) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase ethyl acetate: Acetic acid: HCOOH: H2O [10/1.1/1.1/2.4] Sample Preparation Method 0.3 g + 3 ml 70% grain EtOH sonicated + heated @ 50° C ~ 1 hr Detection Method Natural Product Reagent + PEG -> UV 365 nm Reference see British Pharmacopoeia, 2003
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org. http://www.tropicos.org/Image/61762
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000914115
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000914116
- ↑ United States Dispensatory (1918)
- ↑ Roy Upton, American Herbal Pharmacopoeia® http://www.herbal-ahp.org/
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ American Herbal Pharmacopoeia® http://www.herbal-ahp.org/
- ↑ American Herbal Pharmacopoeia® http://www.herbal-ahp.org/
- ↑ American Herbal Pharmacopoeia® http://www.herbal-ahp.org/
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Claudia Borst, PhytoLab http://www.phytolab.com/en.html
- ↑ Claudia Borst, PhytoLab http://www.phytolab.com/en.html}
- ↑ Claudia Borst, PhytoLab http://www.phytolab.com/en.html
- ↑ Claudia Borst, PhytoLab http://www.phytolab.com/en.html
- ↑ Indena S.p.A. http://www.indena.com/
- ↑ Indena S.p.A. http://www.indena.com/
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- Botanical
- Clusiaceae
- Media
- Voucher
- MOBOT, Tropicos.org.
- Botanical Voucher Specimen Library, Alkemists Laboratories
- Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
- Organolepsy
- United States Dispensatory (1918)
- Macroscopy
- Roy Upton, American Herbal Pharmacopoeia®
- PlantaPhile
- American Herbal Pharmacopoeia®
- Microscopy
- Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories
- Claudia Borst, PhytoLab
- Indena S.p.A.
- HPTLC
- HPTLC Association