Panax ginseng (root)
m (Italicized scientific name) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=HPTLC Entries= | =HPTLC Entries= | ||
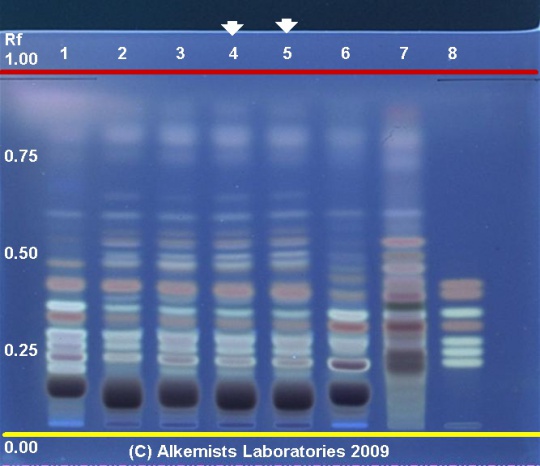
| + | {{HPTLC | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
| + | | description=Asian Ginseng (root) (''Panax ginseng'') | ||
| + | | companyimage=AP-LOGO-Laboratories Crop - Copy.jpg | ||
| + | | companyURL=http://www.alkemist.com | ||
| + | | mainimage=Panax_ginseng_-_Alkemists_Laboratories.jpg | ||
| + | | caption1=''Panax ginseng'' HPTLC ID - 10% Methanolic Sulfuric Acid UV 365 nm | ||
| + | | stationaryphase=Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates | ||
| + | | mobilephase=chloroform: ethyl acetate: CH3OH: water [3/8/4.4/1.8] | ||
| + | | prep=0.3 g + 3 ml 70% grain EtOH sonicate 10 minutes no heat | ||
| + | | detection=10% Methanolic H2SO4 -> 115° C 15 min -> UV 365 nm | ||
| + | | lanes= Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample): | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-1 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-2 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-3 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-4 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-4 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax quinquefolius''-5 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL ''Panax ginseng''-6 (root) | ||
| + | # 2 μL Ginsenoside-Rb1, Ginsenoside-Rc, Ginsenoside-Rd, Ginsenoside-Re, Ginsenoside Rf, Ginsenoside-Rg1 ~0.1% in MeOH | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | | reference=American Herbal Pharmacopoeia & Therapeutic Compendium | ||
| + | | }} | ||
| + | |||
=Other Points of Interest= | =Other Points of Interest= | ||
Revision as of 23:47, 22 October 2012
Contents |
Introduction
Introduction from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Panax_ginseng, retrieved 02/27/2012).
Ginseng (pronounced /ˈdʒɪnsɛŋ/[1]) is any one of eleven species of slow-growing perennial plants with fleshy roots, belonging to the genus Panax of the family Araliaceae.
Ginseng is found only in the Northern Hemisphere, in North America and in eastern Asia (mostly Korea, northern China (Manchuria), and eastern Siberia), typically in cooler climates. Panax vietnamensis, discovered in Vietnam, is the southernmost ginseng known. Ginseng is characterized by the presence of ginsenosides.
The English word ginseng derives from the Chinese term rénshēn (simplified: 人参; traditional: 人蔘). Rén means "man" and shēn means a kind of herb; this refers to the root's characteristic forked shape, which resembles the legs of a man.[2] The English pronunciation derives from a southern Chinese reading, similar to Cantonese jên shên (Jyutping: jan4sam1) and the Hokkien pronunciation "jîn-sim".
The botanical/genus name Panax means "all-heal" in Greek, sharing the same origin as "panacea", and was applied to this genus because Linnaeus was aware of its wide use in Chinese medicine as a muscle relaxant.
Besides Panax ginseng, there are many other plants which are also known as or mistaken for the ginseng root. The most commonly known examples are Xiyangshen, also known as American Ginseng 西洋参 (Panax quinquefolius), Japanese ginseng 东洋参 (Panax japonicus), crown prince ginseng 太子參 (Pseudostellaria heterophylla), and Siberian ginseng 刺五加 (Eleutherococcus senticosus). Although all have the name ginseng, each plant has distinctively different functions. However, true ginseng plants belong to the Panax genus.
The quoted text in this section was licensed for use under the Creative Commons ShareAlike License, version 3.0: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Macroscopic Entries
Microscopic Entries
|
HPTLC Entries
|
Asian Ginseng (root) (Panax ginseng) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference materials used here have been authenticated by macroscopic, microscopic &/or TLC studies according to the reference source cited below held at Alkemists Laboratories, Costa Mesa, CA. Stationary Phase Silica gel 60, F254, 10 x 10 cm HPTLC plates Mobile Phase chloroform: ethyl acetate: CH3OH: water [3/8/4.4/1.8] Sample Preparation Method 0.3 g + 3 ml 70% grain EtOH sonicate 10 minutes no heat Detection Method 10% Methanolic H2SO4 -> 115° C 15 min -> UV 365 nm Reference see American Herbal Pharmacopoeia & Therapeutic Compendium
|
Other Points of Interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found