Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (leaf)
(add PlantaPhile references) |
(add macro characteristics) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=Macroscopic Characteristics= | =Macroscopic Characteristics= | ||
| + | {| border=1 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Macroscopy | source=American Medicinal Plants of Commercial Importance (1930) | ||
| + | | description=The bearberry is a low, much-branched shrub trailing over the ground and having numerous leathery evergreen leaves about 1 inch in length. The waxy flowers, which appear in May, are few and are borne in short, drooping clusters at the ends of the branches. They are white with a pinkish tinge, 5-lobed, and somewhat bell-shaped in form. Smooth, red, globular fruits containing five nutlets follow the flowers. | ||
| + | }} | ||
{{ Media2 | cat=Macroscopy | {{ Media2 | cat=Macroscopy | ||
| source=PlantaPhile | | source=PlantaPhile | ||
| Line 42: | Line 47: | ||
| companyURL2=http://plantaphile.com/ | | companyURL2=http://plantaphile.com/ | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
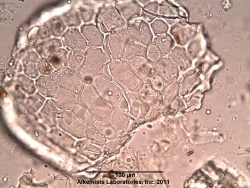
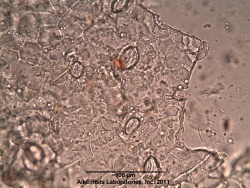
=Microscopic Characteristics= | =Microscopic Characteristics= | ||
{{Media2 |cat=Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | {{Media2 |cat=Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories | ||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 16 June 2015
Contents |
Nomenclature
Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (L.) Spreng. Ericaceae
Standardized common name (English): uva-ursi
Botanical Voucher Specimen
 |
|
|
|
|
Organoleptic Characteristics
Macroscopic Characteristics
|
Microscopic Characteristics
 |
 |
|
|
|
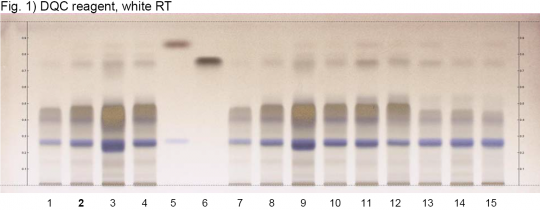
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification
|
Uva-ursi (leaf) (Arctostaphylos uva-ursi) Lane Assignments Lanes, from left to right (Track, Volume, Sample):
Reference Sample(s) Reference: Dissolve 2.5 mg of arbutin in 1 mL of methanol. Dissolve 2.5 mg of hydroquinone in 1mL of methanol. Optional: Dissolve 2.5 mg of gallic acid in 1 mL of methanol. Stationary Phase Stationary phase, i.e. Silica gel 60, F254 Mobile Phase Ethyl acetate, formic acid, water 88:6:6 (v/v/v) Sample Preparation Method Sample: Mix 500 mg of powdered sample with 5 mL of methanol-water 1:1 and sonicate for 10 minutes at 60°C, then centrifuge or filter the solutations and use the supernatants / filtrates as test solutions. Derivatization reagent: 2,6-Dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide (DQC) reagent Preparation: 250 mg of DQC are dissolved in 50 mL of methanol. Use: Spray, dry in a stream of cold air for 3 min, expose to ammonia vapor (hold plate in a tank saturated with 32% ammonia) for 2 s or until blue zones are visible. Detection Method Saturated chamber; developing distance 70 mm from lower edge; relative humidity 33% Other Notes Images presented in this entry are examples and are not intended to be used as basis for setting specifications for quality control purposes. System suitability test: Arbutin: blue zone at Rf ~ 0.27. Hydroquinone: brown zone at Rf ~ 0.87. Identification: Compare result with reference images. The fingerprint of the test solution is similar to that of the corresponding botanical reference sample. Additional weak zones may be present. The chromatogram of the test solution shows an intense blue zone at Rf ~ 0.27 corresponding to reference substance arbutin. Above it there is another blue zone Rf ~ 0.40 and overlapping a very broad and diffuse brown zone. A faint brown zone is seen at Rf ~ 0.75 (gallic acid). Some samples show a faint brown zone at Rf ~ 0.87 (hydroquinone).
|
Supplementary Information
Sources
- ↑ MOBOT, Tropicos.org http://www.tropicos.org/Image/100131549
- ↑ Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://specimens.kew.org/herbarium/K000534677
- ↑ American Medicinal Plants of Commercial Importance (1930)
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ PlantaPhile http://plantaphile.com/
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ Elan M. Sudberg, Alkemist Laboratories http://www.alkemist.com
- ↑ HPTLC Association http://www.hptlc-association.org/