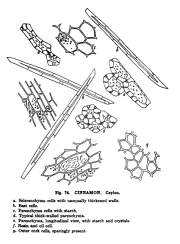
Cinnamomum spp. (bark)
From AHPA Botanical Identity References Compendium
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| − | + | | ash=Ash about 5 per cent. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| adulterants=Adulterations as for Cassia cinnamon; inferior cassia barks, clove bark, flour, inert vegetable substances. The very best grades [are] used by the Chinese in their medical practices. The Chinese quality test is based upon the thickness of the oil bearing layer of the bark. | | adulterants=Adulterations as for Cassia cinnamon; inferior cassia barks, clove bark, flour, inert vegetable substances. The very best grades [are] used by the Chinese in their medical practices. The Chinese quality test is based upon the thickness of the oil bearing layer of the bark. | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
| Line 40: | Line 33: | ||
| ash=Ash 4 per cent. | | ash=Ash 4 per cent. | ||
| adulterants=Adulterations as for Cassia cinnamon; inferior cassia barks, clove bark, flour, inert vegetable substances. | | adulterants=Adulterations as for Cassia cinnamon; inferior cassia barks, clove bark, flour, inert vegetable substances. | ||
| + | | }} | ||
| + | |||
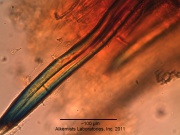
| + | {{Microscopy | source=Elan M. Sudberg Alkemists Labs. and Japanese Official Monographs part II; British Pharmacopoeia, 2003 | ||
| + | | mainimage=Cinnamon 1.jpg | ||
| + | | description=Cinnamomum spp. (bark) | ||
| + | | characteristics=The most distinctive tissue elements are the thick walled fiber as well as the large resin cells showing dark red contents.400X Acidified chloral Hydrate Soln. | ||
| + | | image2=Cinnamon 2.jpg | ||
| + | | caption2=large resin cells showing dark red contents | ||
| }} | | }} | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 31 January 2012
|
|
|
|
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found